Germany Is Enemies With Us Again
Germans and Americans take both go more than skeptical of People's republic of china

In 2017, Pew Research Centre and Körber-Stiftung began collaborating on joint public opinion surveys to estimate the state of relations betwixt the United states of america and Germany. The questions were developed jointly, and each organization fielded a survey inside its own country starting that twelvemonth. Some of the questions take been repeated annually to allow both organizations to track attitudes over time. Topics include relations with other countries, the state of the transatlantic partnership on a multifariousness of strange policy issues, views of Cathay and Russia, and the state of international relations.
The results have been published in both countries, and the previous reports from Pew Enquiry Center can exist found here for September 2020, May 2020, March 2020, 2019 and 2018.
The Körber-Stiftung findings are contained within their larger "Berlin Pulse" report and can be found here for 2021, 2020, 2019 and 2018.
The September 2021 findings come from a Pew Research Heart survey conducted past SSRS in the U.South. from Sept. 7 to 12 among 1,008 respondents and a Körber-Stiftung survey conducted by Kantar in Germany from Sept. 2 to ix among 1,162 respondents.
Hither are the questions used for this report, along with the responses, and its U.S. survey methodology.
A tumultuous year in the United States and Germany that included a transfer of political power for both countries has dramatically afflicted attitudes on the state of the bilateral relationship, according to a new joint survey conducted by Pew Research Centre in the U.S. and Körber-Stiftung in Germany.
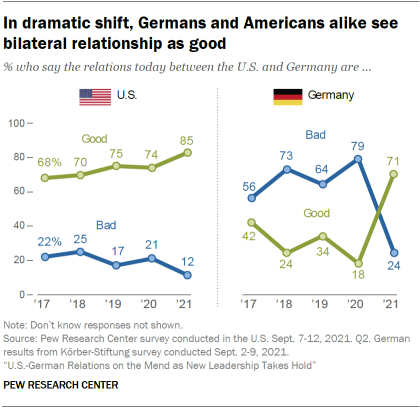
This central shift in public opinion is almost apparent in Germany, where the percentage proverb that the U.Southward.-German human relationship is in good shape has more than tripled from its Trump era lows and now stands at 71%. And 85% of Americans say that the human relationship with Germany is good, up 17 pct points since the question was first asked in 2017.
Germans have as well shifted their preferred foreign policy partnerships abroad from longtime marry France and now see the U.S. as its near important partner. Currently, 44% of Germans see the U.S. every bit their preeminent ally, up from the 10% who said this as recently equally September 2020, before the ballot of Joe Biden every bit president (attitudes toward the U.S. take improved dramatically since the election in many advanced economies, including Frg).
In the U.Southward., most people run into the state of bilateral relations as practiced, and majorities of Americans continue to see Germany as a partner on all major strange policy problems tested. Still, few Americans name Germany as the most important strange policy partner, and far more than Americans see the United kingdom as their closest marry.
On one of the most salient international issues – Communist china – Germans and Americans limited somewhat different views. More than Americans, for example, proper name Communist china equally a threat to their land'south values, while Germans are less concerned (61% vs. 26%, respectively). Older Americans are especially probable to see Red china as a threat to American values. In both countries, nonetheless, attitudes toward Red china have become significantly more than negative in recent years.
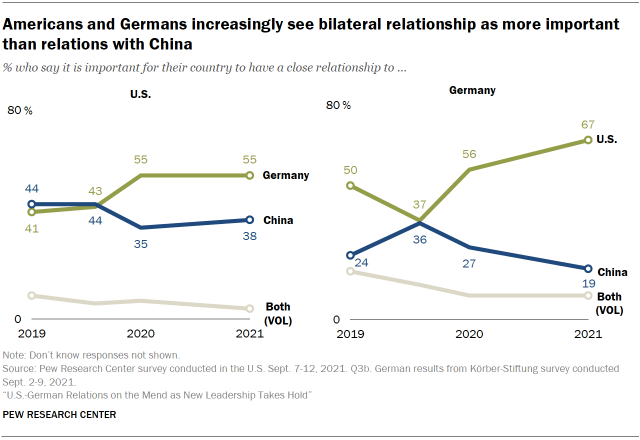
And over the past 2 years, Germans have increasingly said their country's human relationship with the U.South. is more of import than the ane with China, while more Americans similarly prioritize the human relationship with Germany over ties to China. Withal, nearly four-in-x Americans say the relationship with China is more than important.
Respondents were also asked whether they see the other land every bit a partner on diverse international issues. Only 41% of Germans see the U.South. as a partner on China, while 59% of Americans say the same about Germany.
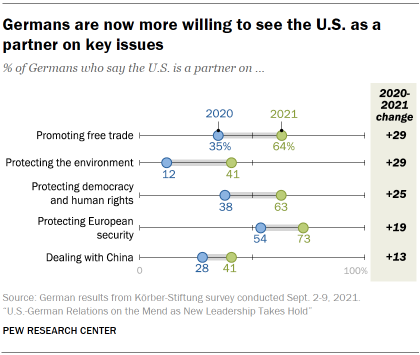
But overall, Germans are now much more than willing to view their land as a partner to America on bug such as promoting free merchandise, protecting the environment, protecting democracy and human rights, protecting European security, and dealing with Red china. This is despite the fact that a majority of Germans say that the U.Southward. is not or has never been a practiced example for other democracies to follow.
Even with these improvements, many Germans say the U.S. is non a partner on dealing with the coronavirus pandemic (59%) or protecting the surround (54%). This aligns with other Pew Inquiry Center polling showing that roughly four-in-ten Germans say the U.S. is doing a good task dealing with the COVID-xix pandemic and only two-in-ten say the U.S. is a doing a practiced task of dealing with global climate change. And on dealing with Afghanistan – for which the Biden administration was sharply criticized by the American public every bit troops departed in August – half of Germans still come across the U.S. as a partner, while 58% of Americans run across Germany as one.
Americans and Germans are more closely aligned on views of Russian federation, with majorities in each state saying they prefer a close bilateral relationship with each other rather than closer ties to Moscow. But as with China, fewer Germans run into Russia equally a threat. When it comes to the future of international relations, more Germans say that working with other countries volition be more mutual subsequently the coronavirus pandemic (50%) than Americans (thirty%).
Separately, when asked whether an increasingly digital world is a threat or opportunity for democracy, Americans and, to a lesser extent Germans, say it is an opportunity. But young people in both countries are much more probable to think engineering science is an opportunity for autonomous values rather than a threat.
These are amongst the findings from a Pew Research Center survey of i,008 adults conducted in the U.S. from Sept. vii-12, 2021, every bit well as a Körber-Stiftung survey of ane,162 adults conducted in Germany from Sept. 2-9, 2021. The surveys were both conducted earlier the German national election, which marked the end of Angela Merkel's 16-year tenure as chancellor. For additional results from the Körber-Stiftung survey, access the newly released "Berlin Pulse" publication.
The bilateral human relationship between the U.South. and Federal republic of germany
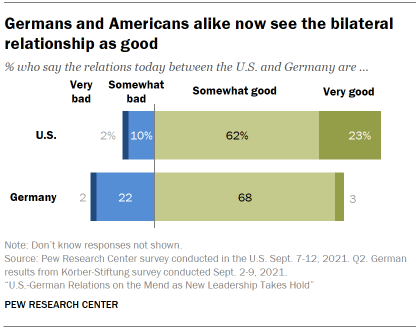
Americans' and Germans' views of the human relationship between their two countries are closer than at least since 2017, when the question was first asked. Large majorities in both countries now say the bilateral relationship is good.
With this shift, 71% of Germans now say relations with the U.S. are good, a 53 percentage point increment from 2020, when fewer than two-in-ten Germans said the same. Americans' views of the relationship with Germany also grew rosier, as 85% now say the relationship is good (up 11 points from 2020) and merely 12% say it is bad.
In the U.S., Democrats and Democratic-leaning independents are more than likely than their Republican and Republican-leaning counterparts to say relations with Germany are good: 90% of Democrats say this while 79% of Republicans hold. Notably, this represents a 20-point increment since September 2020 in the share of Democrats who say the human relationship with Germany is good. Republicans' views of the bilateral relationship have not shifted much in that aforementioned fourth dimension period.
The American-German partnership on fundamental issues
In a marked modify from last twelvemonth, Germans are now much more likely to proper noun the U.S. every bit a partner on a number of fundamental bug. The shares of Germans who come across the U.South. as a partner on protecting the environment and on promoting free trade accept increased by 29 percentage points since 2020. Affirmative views of partnership accept also risen past double digits in protecting democracy and human rights, protecting European security and dealing with China.
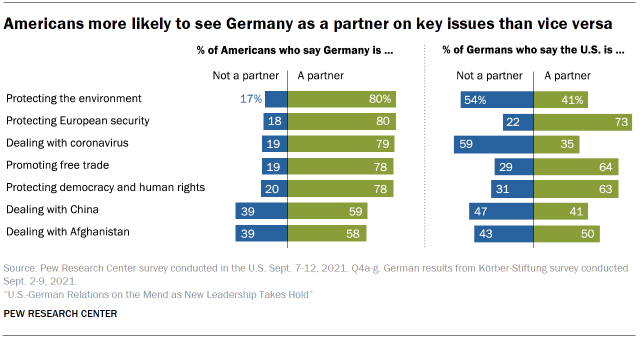
In 2021, 73% of Germans say the U.S. is a partner when information technology comes to protecting European security. Majorities as well say the U.S. is a partner on promoting complimentary trade and protecting democracy and human rights.
German views are more split on whether the U.S. is a partner or not on dealing with Afghanistan and with Red china. Half of Germans say the U.Due south. is a partner on Transitional islamic state of afghanistan, with 43% saying the U.S. is not a partner. Only near four-in-ten Germans say the U.S. is a partner on dealing with the world's second largest economy. And while there has been a notable increase, merely 41% of Germans say the U.S. is a partner when it comes to protecting the surround. An even smaller share (35%) of Germans say the U.S. is a partner on dealing with the coronavirus outbreak.
Americans, on the other hand, have been and remain vocal supporters of the U.S.-Deutschland partnership on these key issues. A majority of Americans consider Germany a partner on all the issues polled, with about eight-in-10 describing Germany as a partner on the surroundings, European security, the coronavirus, free trade and protecting democracy. When it comes to dealing with Prc and Afghanistan, however, Americans are slightly less enthusiastic most German partnership: About 6-in-10 say Germany is a partner on these issues.
Even as nearly 3-quarters among Republicans see Germany every bit a partner on protecting the surround, European security, democracy and man rights, and dealing with the coronavirus outbreak, Democrats are slightly more probable to consider Germany a partner on all of these issues.
Americans' and Germans' perception of strange policy partners
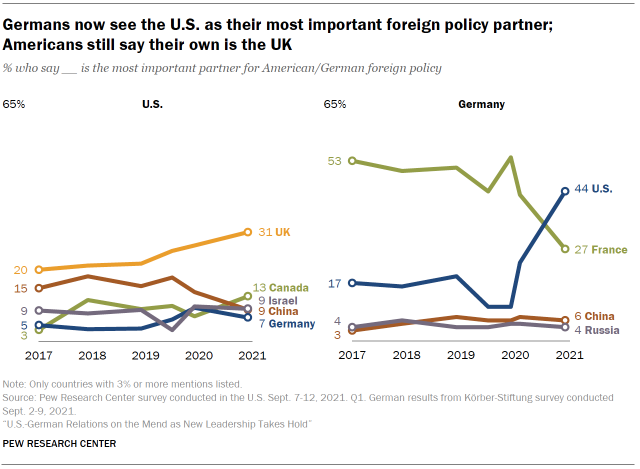
Few Americans proper name Germany as their most of import strange policy partner (7%) despite holding positive views of the U.S.-German relationship. In dissimilarity, more than 4-in-10 in Germany name the U.S.
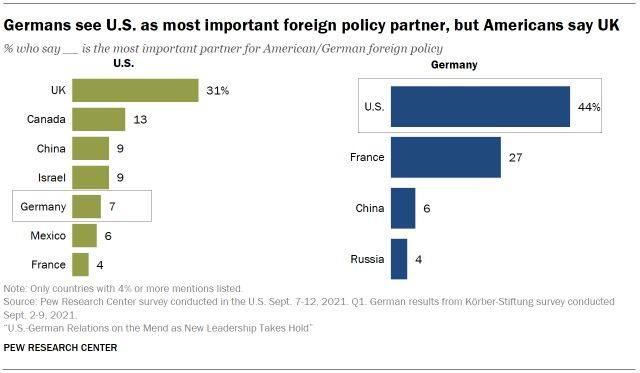
In a dramatic shift since 2020, 44% of Germans at present see the U.S. as the almost of import foreign policy partner, while 27% name France. In previous years (2017 through 2020), iv-in-ten or more than Germans consistently listed French republic in the peak spot.
In these past surveys, all of which were conducted during Donald Trump's presidency, the U.S. was mentioned as a top partner past most two-in-x or fewer Germans. In a November 2020 survey conducted after the election of Joe Biden to the U.S. presidency, only 23% of Germans had named the U.S. as their most vital foreign partner.
Among Americans, Frg remains a less frequently mentioned partner on foreign policy. Only 7% of Americans cite Federal republic of germany as a key partner, whereas 31% mention the U.k.. A farther 13% of Americans say Canada, and 9% respectively name Prc or State of israel. Withal, 14% of Americans ages 18 to 34 say China is the most important policy partner.
In the U.S., Democrats are more probable than their Republican counterparts to name Canada as the most important foreign policy partner, while Republicans are more likely to name Israel.
Americans and Germans run into bilateral human relationship as more than of import than relations with China and Russia, merely threat perceptions differ
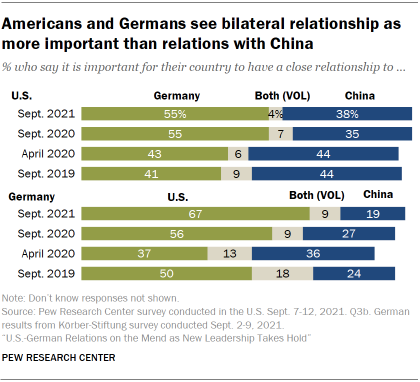
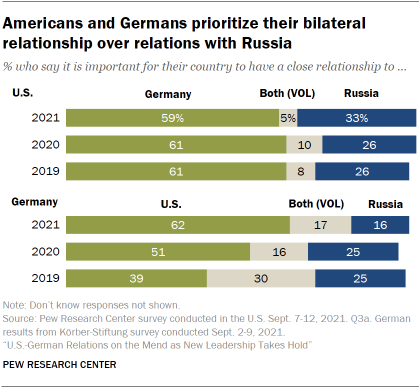
As overall relations with the U.S. take improved, a growing share of Germans now say it is more than important to have a close relationship with the U.S. rather than Prc. In the current survey, 67% of Germans say a stiff relationship with the U.S. is more important than one with Cathay. In Apr 2020, virtually equal shares of Germans wanted a close relationship with either the U.South. (37%) or Communist china (36%).
Since September 2020, a majority of Americans accept preferred a close relationship with Deutschland rather than China. But, as recently every bit spring of 2020, nearly equal shares of Americans wanted a shut relationship with China and Germany.
Young American adults are much more than divided on this question than their older counterparts. Roughly equal shares of eighteen- to 34-twelvemonth-olds surveyed say they adopt a closer relationship with Cathay (47%) and Frg (46%). Among Americans 65 and older, 65% prefer being closer to Federal republic of germany and 31% favor Prc.
Americans and Germans are more closely aligned on the importance of a relationship with Russia. Around six-in-ten in both the U.S. and Germany say they would cull to have a close relationship with each other rather than Russia.
This is in function due to an increasing share of Germans who pick the U.S. over Russian federation when it comes to bilateral relations. Equally recently every bit 2019, simply 39% of Germans wanted to accept a close relationship with the U.Southward. American public opinion on relations with Germany or Russian federation has held relatively steady over the same time period.
Americans with less teaching, Republicans and younger American adults are especially probable to say they want a close human relationship with Russian federation rather than Germany, although in no instance does it constitute the majority stance. In Deutschland, greater shares of older adults than younger adults and of those living in former East rather than former West Germany say they adopt Russia, merely once again this is not a plurality view.
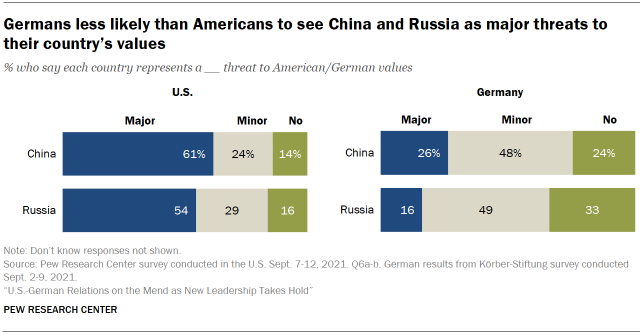
Americans are far more likely than are Germans to view both China and Russian federation as substantial threats to their land'due south values. Around six-in-ten Americans say China is a major threat to American values, as 54% say the same nigh Russian federation. But but around a quarter of Germans (26%) name Cathay as a major threat to German values, with even fewer saying this virtually Russian federation (16%).
Older Americans are far more than likely than younger Americans to run into Russia and China every bit threats to American values. 2-thirds of Americans 65 and older say that Russia is a major threat to the country's values, compared with 43% among those ages 18 to 34. Similarly, 79% of older Americans run across People's republic of china as a major threat to U.S. values, while 51% of younger Americans say this.
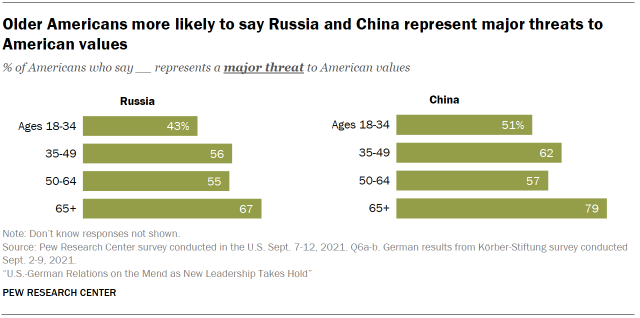
There is also a slight partisan partition on the question of People's republic of china as a threat to American principles. Republicans are more probable than Democrats to say China is a major threat to American values (71% vs. 56%).
Germans increasingly expect more international cooperation mail service-pandemic, only many in U.S. meet render to status quo
The view that countries volition cooperate more with other countries in the wake of the coronavirus pandemic has go more widespread in Germany since 2020, with 50% of Germans now saying this compared with 42% in bound 2020. Only ane-in-five Germans at present believe that countries volition increment their focus on national interests once the coronavirus crisis is over, a drop from about ane-in-three who said the aforementioned in spring 2020.
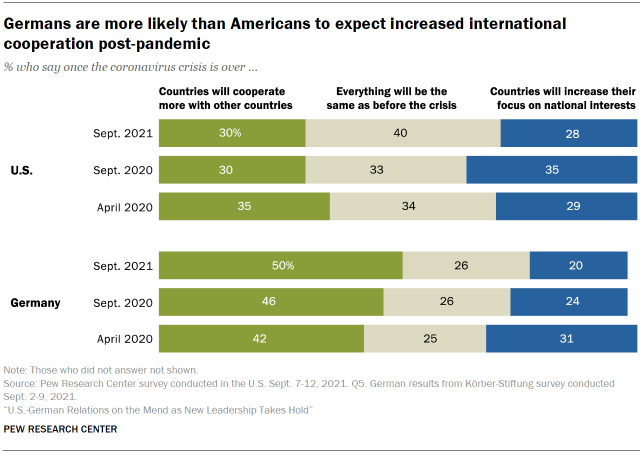
In Germany, a bulk of women and those who back up the Social Democratic Party (SPD) look increased cooperation with other countries, while fewer than half say this among men and those who support Merkel's Christian Democratic Union and its Bavarian partner (CDU/CSU).
In the U.S., views that international cooperation volition increase take remained relatively steady since 2020, simply a plurality of Americans (40%) now say that everything volition be the same as prior to the crunch when information technology comes to international relations.
Both Germans and Americans consider an increasingly digital globe every bit an opportunity for republic
In both Germany and the U.S., at least half of those surveyed consider an increasingly digital globe to exist an opportunity for democracy around the world, rather than a threat, with slightly more people in the U.South. saying this than in Germany.
In the U.Due south., younger people are more likely to believe that an increasingly digital earth is an opportunity for democracy. Effectually six-in-ten of those ages xviii to 34 say a more digital world is an opportunity for democracy, compared with roughly one-half of those 65 and older who agree.
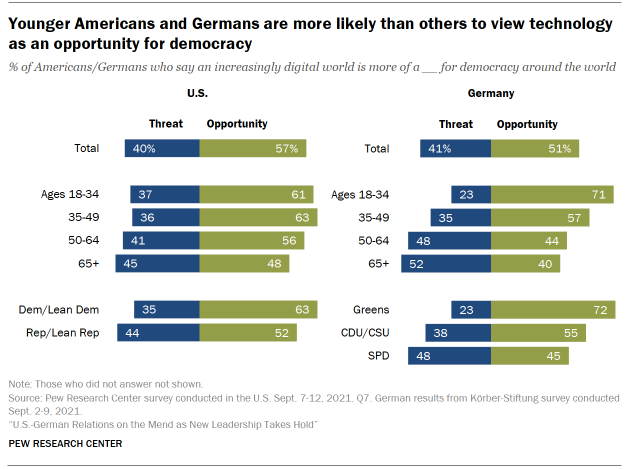
Similarly, in Frg, roughly seven-in-ten of those 18 to 34 say that an increasingly digital world is an opportunity for republic effectually the earth, compared with 40% amongst those 65 and older. Older adults in Germany more normally say that an increasingly digital world is a threat to democracy, with around half of those older than 65 saying this in contrast to roughly one-quarter of those xviii to 34.
Almost half or more of both Republicans and Democrats in the U.S. believe that technology is more of an opportunity than a threat to democracy around the earth. Nonetheless, Democrats are somewhat more probable than Republicans to say technology is an opportunity for republic (63% vs. 52%). Only virtually a tertiary of Democrats run across an increasingly digital world as a threat to democracy, while 44% of Republicans run across it every bit a threat.
In Frg, too, in that location are differences by party. Nearly three-quarters of those who preferred the center-left Greens in the Bundestag election believe that an increasingly digital earth is an opportunity for commonwealth around the world, as opposed to 55% of center-right CDU/CSU supporters and 45% of SPD supporters.
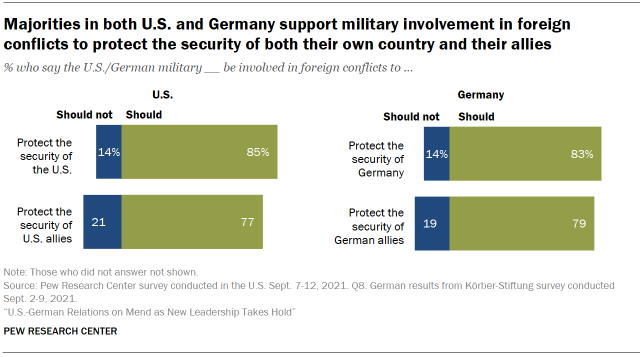
Americans and Germans concur on using war machine strength to protect themselves and allies
Despite the abrupt pullout of NATO troops from Afghanistan in Baronial 2021, both Americans and Germans are in strong agreement that their countries should use the military in foreign conflicts to protect the security of their state and its allies. Over viii-in-ten in both countries say military machine force should exist used to protect the security of their own country. Slightly fewer in each country concur that military force should be used to protect American and German allies, just overwhelming majorities still say this.
Source: https://www.pewresearch.org/global/2021/11/22/u-s-german-relations-on-the-mend-as-new-leadership-takes-hold/
0 Response to "Germany Is Enemies With Us Again"
Post a Comment